A website consists of many files: text content, code, stylesheets, media content, and so on. When you're building a website, you need to assemble these files into a sensible structure on your local computer, make sure they can talk to one another, and get all your content looking right before you eventually upload them to a server. Dealing with files discusses some issues you should be aware of so you can set up a sensible file structure for your website.
When you are working on a website locally on your computer, you should keep all the related files in a single folder that mirrors the published website's file structure on the server. This folder can live anywhere you like, but you should put it somewhere where you can easily find it, maybe on your Desktop, in your Home folder, or at the root of your hard drive.
You'll notice that throughout this article, we ask you to name folders and files completely in lowercase with no spaces. This is because:
File names also map to URLs. For example, if you have a file called my_file.html at the root of your server-served directory, generally it will be accessible at https://example.com/my_file.html by most web servers' default behavior. Some servers will replace the spaces in your filenames with "%20" (the character code for spaces in URLs), which can create subtle bugs with some server-side logic if they assume that file names and URLs match perfectly.
It's also advisable to separate words with hyphens, rather than underscores: my-file.html vs. my_file.html . The Google search engine treats a hyphen as a word separator but does not regard an underscore that way. This can be remedied by configuring your server to replace underscores with hyphens, but that's extra work and more bug-prone with diverging file names and URLs.
For these reasons, it is best to get into the habit of writing your folder and file names in lowercase with no spaces and with words separated by hyphens, at least until you know what you're doing. That way, you'll encounter fewer problems down the road.
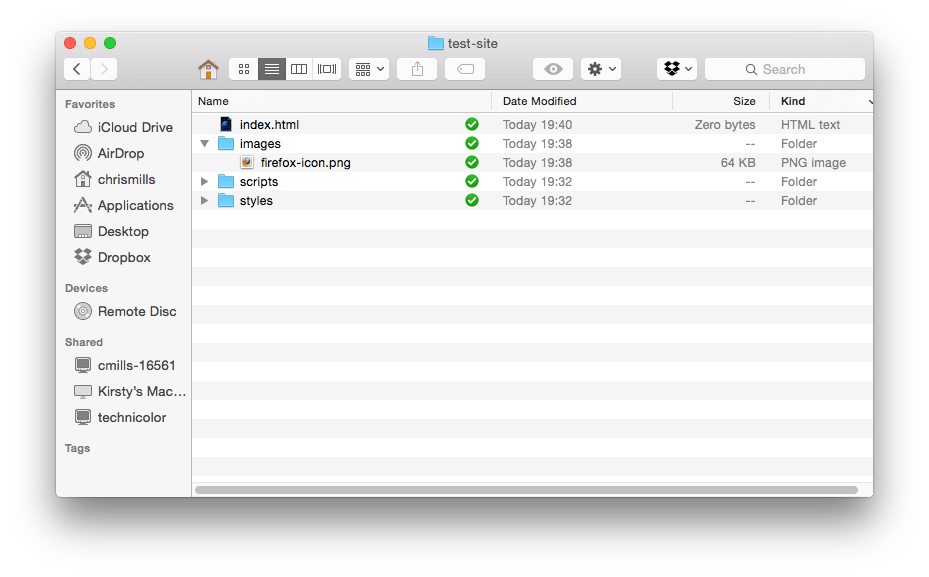
Next, let's look at what structure our test site should have. The most common things we'll have on any website project we create are an index HTML file and folders to contain images, style files, and script files. Let's create these now:
Note: On Windows computers, you might have trouble seeing the file names, because Windows has an option called Hide extensions for known file types turned on by default. Generally, you can turn this off by going to Windows Explorer, selecting the Folder options… option, unchecking the Hide extensions for known file types check box, then clicking OK. For more specific information covering your version of Windows, you can search on the web.
To make files talk to one another, you have to provide a file path between them — basically a route, so one file knows where another one is. To demonstrate this, we will insert a little bit of HTML into our index.html file, and make it display the image you chose in the article "What will your website look like?" Alternatively, you can choose an existing image at your disposal, on your computer or from the Web, and use it in the following steps:
doctype html> html lang="en-US"> head> meta charset="utf-8" /> meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> title>My test pagetitle> head> body> img src="" alt="My test image" /> body> html>
My test image">

Some general rules for file paths:
For now, this is about all you need to know.
Note: The Windows file system tends to use backslashes, not forward slashes, e.g. C:\Windows . This doesn't matter in HTML — even if you are developing your website on Windows, you should still use forward slashes in your code.
That is about it for now. Your folder structure should look something like this: